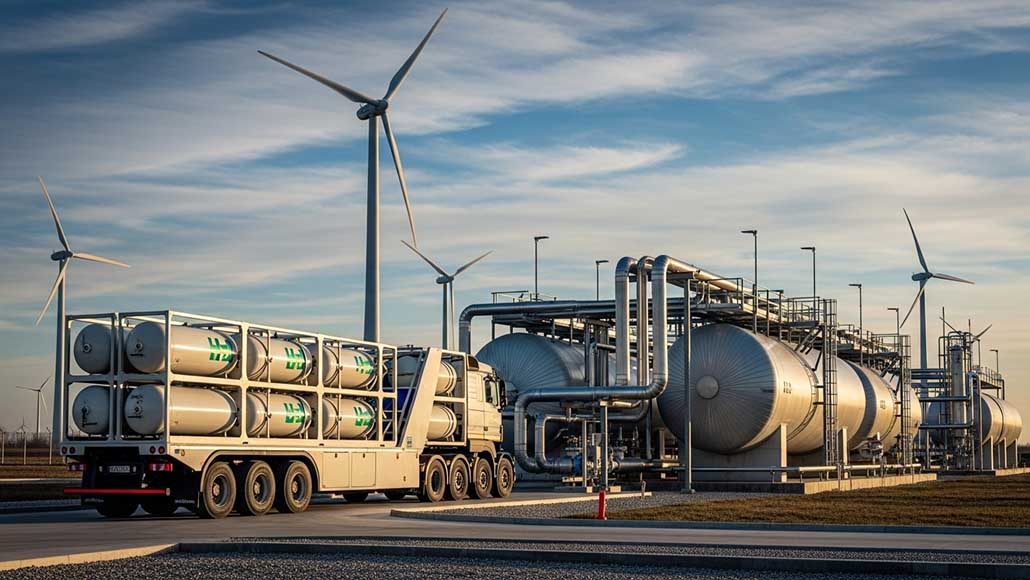
As the hydrogen economy gathers momentum, hydrogen storage and transportation solutions are emerging as critical enablers for scaling production and usage. Hydrogen’s potential as a clean, versatile fuel is undeniable, but its low density and flammability require specialized storage and delivery methods. Recent innovations are addressing these challenges, making hydrogen safer, more efficient, and more cost-effective to move from production sites to end users.
Advances in Hydrogen Storage
One of the most significant breakthroughs in hydrogen storage and transportation solutions is the development of high-pressure composite tanks. These lightweight, carbon-fiber-reinforced containers can store hydrogen at pressures up to 700 bar, enabling greater fuel density and longer driving ranges for hydrogen fuel cell vehicles. Advances in tank design have improved safety, reduced manufacturing costs, and extended lifespan, making them viable for both mobility and stationary applications.
Liquid hydrogen storage is another area gaining traction, particularly in the aerospace and shipping sectors. By cooling hydrogen to -253°C, its volume is reduced by nearly 800 times, enabling more efficient bulk transportation. Recent innovations in cryogenic insulation and boil-off gas management have made liquid hydrogen storage more practical and cost-competitive.
Researchers are also exploring solid-state hydrogen storage using metal hydrides, porous carbon materials, and advanced alloys. These materials absorb and release hydrogen at lower pressures, offering safer and potentially cheaper alternatives for large-scale energy storage. Solid-state solutions could become particularly important for stationary power generation and remote area supply.
Transforming Hydrogen Transportation
Pipeline transport remains one of the most efficient ways to move hydrogen, especially for large volumes. Several countries are upgrading natural gas pipelines to handle hydrogen blends or building dedicated hydrogen pipelines. Advanced materials and coatings are being developed to prevent embrittlement, a common challenge when transporting hydrogen through steel pipes.
For regions without pipeline infrastructure, innovations in hydrogen storage and transportation solutions include liquid organic hydrogen carriers (LOHCs). These chemical compounds can store hydrogen in a stable liquid form at ambient conditions, allowing it to be transported using conventional fuel logistics. Upon arrival, the hydrogen can be released for use in fuel cells or industrial processes.
Hydrogen shipping is also advancing with the deployment of purpose-built liquid hydrogen tankers. Japan’s Suiso Frontier, for example, is pioneering international hydrogen trade by carrying liquid hydrogen from Australia to Japan.
Future Outlook
As global hydrogen demand grows, innovations in hydrogen storage and transportation solutions will be crucial to connecting renewable hydrogen production sites with industrial hubs, transportation fleets, and power systems. With ongoing R&D in materials science, cryogenics, and chemical storage methods, the cost and complexity of moving hydrogen are expected to drop significantly over the next decade.
By combining advances in storage and transportation, the hydrogen industry can overcome one of its most persistent challenges, accelerating the transition toward a low-carbon, hydrogen-powered future.