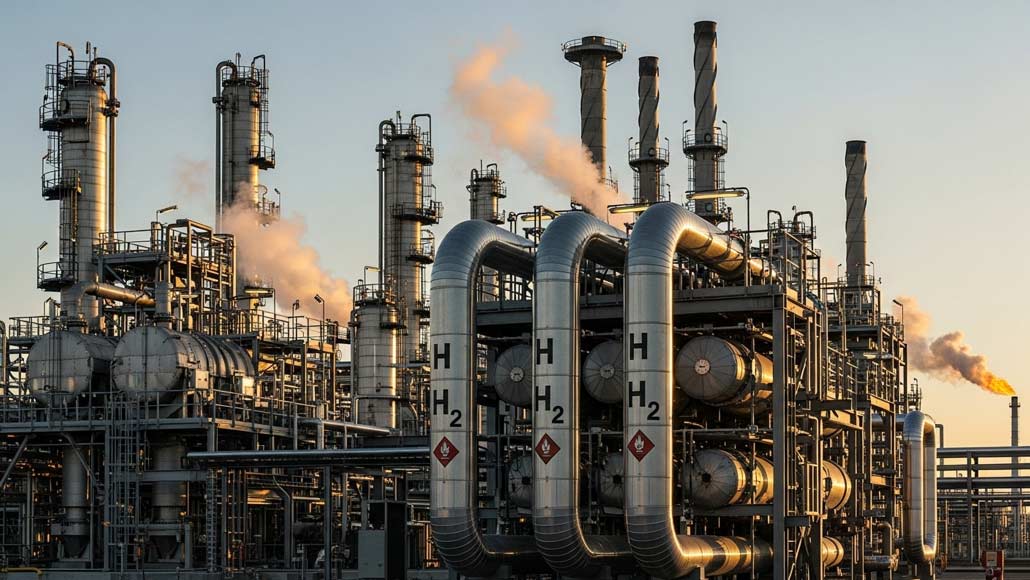
As the global economy shifts towards sustainability, decarbonization has gone on to become a central pillar of industrial transformation, specifically within the refining as well as chemical sectors. These industries are historically quite substantial emitters when it comes to greenhouse gases because of their dependence on fossil fuels and energy-intensive processes. Still in the middle of the pressing urgency in order to meet climate targets, hydrogen has emerged as a transformative solution which facilitates the leap towards low carbon and sustainable operations.
The versatility of hydrogen makes it distinctly suited to revolutionise refining as well as chemical manufacturing, especially by way of replacing carbon intensive feedstocks, making sure of industry dependence in changing regulatory spectrum and supporting cleaner energy usage. But the journey towards integrating hydrogen within these sectors is intricate and also multifaceted and needs substantial technological innovation, strategic investment, as well as policy support.
The need for hydrogen in refining and chemical industries
It is well to be noted that refining and chemical manufacturing happen to be among the largest industrial contributors towards global carbon emissions. Traditional processes go on to depend pretty heavily on fossil fuels, both in terms of energy sources as well as raw materials, resulting in substantial greenhouse gases. In terms of refineries, the refining of crude oil into fuels and lubricants, as well as other products, has always been an energy-intensive activity. When it comes to chemical manufacturing, the dependence on petrochemical feedstocks goes on to lead to high emissions, especially when producing basic chemicals, plastics, and fertilizers.
Apparently, the sector goes on to face mounting pressures coming from policymakers, consumers, and investors so as to lower the emissions. Regulatory frameworks across the world are incrementally tightening the emission standards and aiming for net zero objectives within the next decades. In the same way, the rising cost of carbon along with increasing market demand when it comes to green products are incentivizing the industry players in order to innovate.
The potential of hydrogen in this context happens to lie in its capacity to replace the fossil fuels and produce low-carbon feedstocks. Green hydrogen, which is produced by way of using renewable energy through electrolysis can substantial lower the carbon footprint when it comes to Chemical and refining value chain. Its widespread adoption promises not just to meet the regulatory compliance but at the same time to elevate competitiveness by way of decreasing the operational expense and upgrading the market positioning.
Technological pathway for hydrogen integration
The pathway for incorporating the hydrogen within the refining and chemical manufacturing, span different technological domains, which are customised in order to achieve maximal reduction in emissions while at the same time, maintaining the process integrity along with safety.
Hybrid systems where hydrogen, primarily green hydrogen, is made use of alongside traditional fossil fuels and goes to serve as an initial transitional step. For refineries, blending hydrogen along with existing hydrocarbons can decrease the carbon intensity quite significantly without overhauling the present facilities.
The most ambitious pathway goes on to involve replacing the fossil-based feedstock altogether. It is well to be noted that in the case of refining, hydrogen can be employed in order to upgrade the heavy residual oils into cleaner and lighter fuels, therefore reducing the process emissions. When it comes to chemicals, hydrogen goes on to serve as a raw material for producing ammonia and methanol, as well as other critical chemicals, in a much lower-carbon manner.
Electrolysis-driven hydrogen production, which is fueled by renewable energy sources, goes on to remain the cornerstone of green hydrogen supplies. Advancement within the electrolyzer efficiency, teamed with reducing renewable energy expenditure, is making this pathway increasingly viable economically.
Moreover, carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) can complement the usage of hydrogen by way of capturing the emissions coming from existing processes, effectively bridging the gap till the time fully hydrogen-based systems get operational.
Strategic advantages of hydrogen driven decarbonisation
The integration of hydrogen within refining as well as chemical industries happens to furnish numerous strategic benefits. Foremost is aligning along with the worldwide climate commitments by allowing the companies to meet or even exceed regulatory benchmarks and at the same time demonstrating stewardship in the environmental Spectrum. Cost efficiency is increasingly more understandable. As renewable energy as well as electrolysis technologies mature, green hydrogen production expenditures are anticipated to continue to decline by helping with competitive operational costs as compared to fossil fuels. This kind of transition presents financial advantages by way of decreased carbon taxes and emissions trading, as well as potentially profitable green certification markets.
Besides this, the rollout of hydrogen helps with industry resilience in the middle of volatile fossil fuel markets as well as policy transitions. It offers a pathway in terms of diversification, energy security, and even vertical integration as far as the supply chains are concerned.
Functionally, hydrogen makes way for process innovation, thereby helping with cleaner and more agile manufacturing processes. It actually opens the doors to developing new high-value products that are aligned with the growing consumer demand when it comes to environmentally friendly goods.
From a technological standpoint, hydrogen integration catalyzes the broader digital transformation initiatives like predictive maintenance, automation, and also real-time tracking, thereby further optimizing the efficiencies of the plant.
Executing challenges as well as solution
In spite of its promising aspects, embedding hydrogen within refining as well as chemical industries happens to face multifaceted barriers. The high capital investment that is required for electrolyzers and green hydrogen infrastructure, along with process modifications, can be a hurdle specifically in regions where policy incentives are very limited. Technological maturity also varies throughout regions and facilities. Retrofitting existing plants in order to handle hydrogen safely as well as efficiently happens to involve intricate engineering and process redesign as well as safety protocols – all of which require time and also expertise.
Apparently, supply chain development happens to remain a very critical hurdle. Green hydrogen production has to be scaled up pretty significantly, and dependable, cost-effective energy sources should be aligned with the manufacturing locations. Storage along with transportation infrastructure for hydrogen requires further development in addition to safety certifications as well as standards.
The fact is that regulatory frameworks should evolve in tandem with market mechanisms by offering clear pathways for safety, certification, and even pricing that is aligned with the decarbonization objectives. In parallel, the workforce requires reskilling in order to operate as well as maintain hydrogen-ready facilities.
Taking note of such challenges demands partnerships among industry players, academia, and governments. Public-private collaborations, international standards, and innovation funding are going to be critical drivers of this shift.
The future of hydrogen when it comes to industry decarbonization
The future spectrum of the role of hydrogen in decarbonizing of refining and chemicals appears quite promising. With consistent technological advancements, like more efficient electrolyzers, solutions that are innovative, and also digital tracking, green hydrogen is anticipated to become more cost-competitive as compared to fossil fuels. Policy support, which includes carbon pricing as well as subsidies, is likely to speed up that adoption, catalyzing funding as well as infrastructure development. Regional initiatives along with international cooperation is indeed going to foster worldwide hydrogen trade by opening more markets and helping with the transfer of technology.
Moreover, the integration of hydrogen will catalyze wider industrial innovations like carbon capture and digital transformation, as well as advanced process automation, thereby making the sectors more resilient along with being sustainable.
The growing stress on circular economy models as well as sustainable product development is going to stimulate demand when it comes to low-carbon chemicals as well as materials by consolidating the role that hydrogen plays. As sectors reach critical mass, the convergence of technology and policy, as well as market forces, is indeed going to transform hydrogen by making it a very essential component when it comes to being a low-carbon industrial backbone.
In the end
The vital Role which hydrogen plays in the decarbonizing of refining and chemicals is undeniable. It goes on to offer a path towards a much cleaner operation, regulatory compliance, and a resilient supply chain, thereby driving economic as well as environmental sustainability.
As the sector transitions from pilot project to large-scale rollout, the focus has to transition towards fostering technological innovation, developing infrastructure that is supportive, and also forging worldwide partnerships. Strategic investments along with forward-thinking policies are indeed necessary in order to unlock the complete potential when it comes to hydrogen.