Korean researchers have discovered a novel method that could help in solving one of the biggest issues concerning the electrolysis process, which is essential to create hydrogen as an energy source.
As Korean scientist create a catalyst that eradicates the corrosive chloride ions from the electrolysis procedure, it could help with the creation of hydrogen from seawater and freshwater.
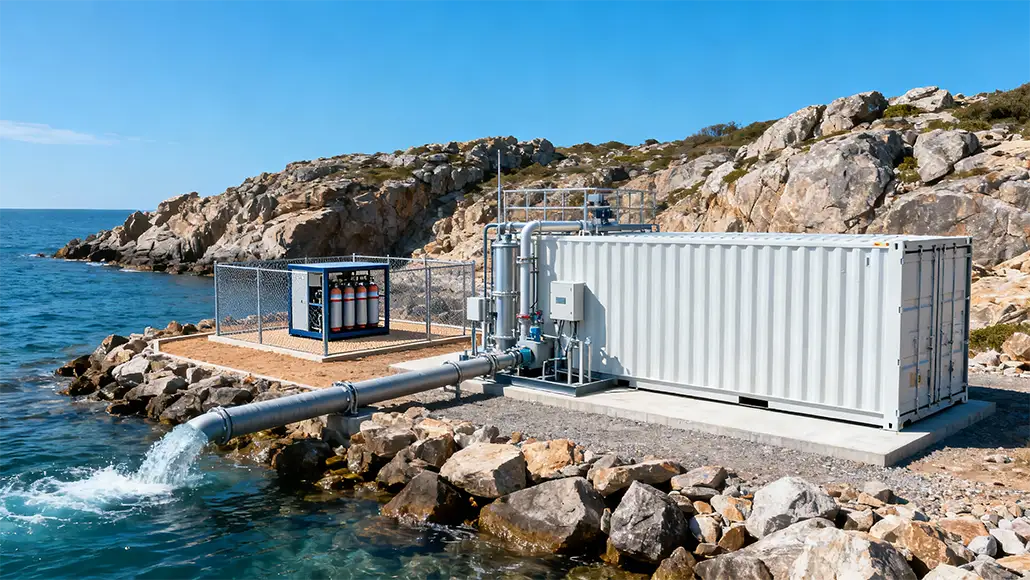
Typically, the electrolysis process happens to work with freshwater. When one makes use of the same methods with saltwater, they happen to be left with not just hydrogen and oxygen but also chloride, which kind of eats away at the electrodes that are needed to split the water and also create pure hydrogen.
KIMS scientists have made use of MXene, which happens to be a two-dimensional nanomaterial that they went on to oxidize before blending it with nickel ferrite. With this Korean scientist create a catalyst that, as per Interesting Engineering, had five times the present density and double the durability of conventional catalysts. It also went on to repel the chloride ions, decreasing the risk of corrosion.
According to Juchan Yang, per IE, the project lead, this study happens to be significant, as it addresses the issue of chloride ions in seawater by way of utilizing the novel material MXene. They are actively conducting follow-up demonstration research so as to advance this technology in a sustainable hydrogen production solution.
Hydrogen, specifically green hydrogen, or hydrogen that is produced with renewable energy, has gone on to gain some attention as the world looks out for more renewable alternatives to oil and gas, therefore aiming to decrease the generation of heat-trapping pollution and also diversify the energy mix. But the drawbacks of the fuel can be quite prominent.
Hydrogen happens to be costly to produce and can also need massive amounts of power, therefore defeating the purpose in terms of creating it in the first place, specifically in the cases wherein dirty fossil fuels happen to be a part of the process. In addition to that, with freshwater becoming a rare and precious commodity across many parts of the warming world, making use of it to create energy happens to pose its own set of challenges.
At the same time, this development may as well open up massive opportunity for hydrogen fuel production so as to become a bigger part of the energy mix, therefore potentially making saltwater a pathway that’s viable for its generation and also making sure that freshwater can get saved for more essential requirements such as drinking as well as irrigation.