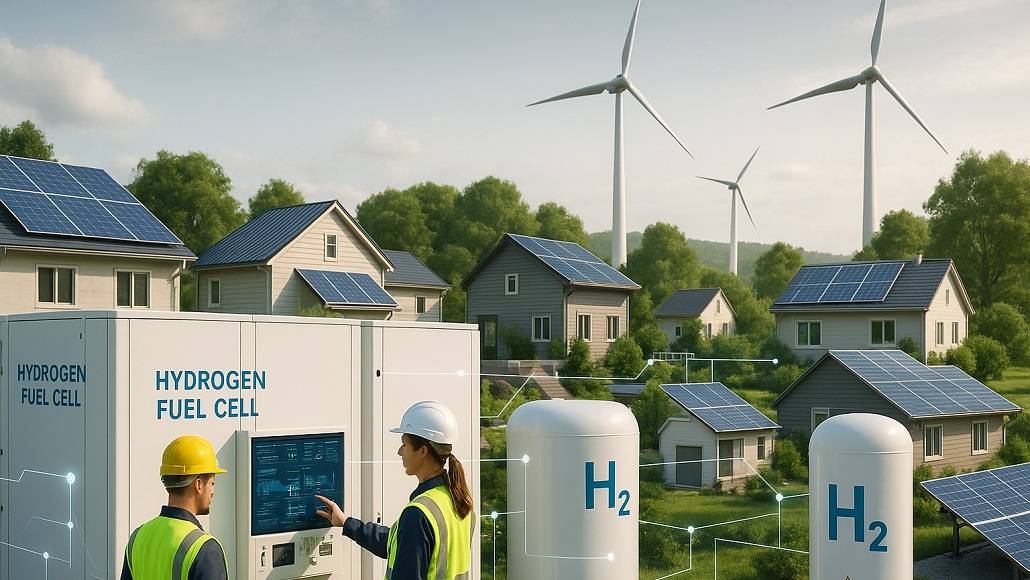
As the global demand for clean, reliable, and decentralized power systems continues to rise, hydrogen microgrids are emerging as a transformative solution. These innovative technologies provide a reliable and sustainable substitute for conventional grid energy by combining the production, storage, and power generation of hydrogen. Designed to provide resilient off-grid power solutions, hydrogen microgrids are perfectly suited for remote locations, critical infrastructure, and areas vulnerable to natural disasters or grid outages.
Hydrogen microgrids operate independently of centralized electricity networks, delivering localized energy that is both efficient and environmentally friendly. Hydrogen microgrids being the energy frontiers promise to simultaneously solve some of the issues pertaining to energy stability, energy security, and emissions pertaining to carbon by virtue of hydrogen being a clean fuel. Since such a position is assumed in theorizing, hydrogen microgrids are seen as being very crucial in the global low carbon transition with technology development and the growth of demand.
The Concept of Hydrogen Microgrids
Hydrogen microgrids are very localized energy systems that use hydrogen as their primary fuel. Power is generated in hydrogen microgrids through hydrogen fuel cells, while traditional microgrids usually use batteries or fossil fuels for energy generation and storage. All these technologies combined with renewable sources of energy such as solar and wind to produce hydrogen through electrolysis.
The hydrogen that is generated is stored in tanks to be used for powering fuel cells during grid disruption events or when the electricity demand is higher than the renewable supply coming from the local solar and/or wind installations. Such a closed-loop system approaches the needs of a smooth uninterrupted supply of energy while having minimal greenhouse gas emissions at the point of consumption.
One important feature of hydrogen microgrids is scalability. They can be designed to meet the energy needs of local municipalities, industrial complexes, or even individual buildings. Their versatility makes them a good choice for a wide range of applications, including disaster recovery and rural electricity.
The Advantages of Hydrogen Microgrids
Hydrogen microgrids are gaining popularity due to their multiple benefits over traditional energy systems. The advantages cover operational, financial, and environmental aspects, demonstrate the technology’s revolutionary potential.
- Sustainability and Emissions Reduction
Hydrogen microgrids are inherently sustainable since hydrogen is generated utilizing renewable energy sources. By using hydrogen instead of fossil fuels, these technologies eliminate carbon emissions at the source of energy. Furthermore, employing renewable energy ensures that the energy cycle remains clean overall, promoting global decarbonization goals.
- Energy Independence and Security
Hydrogen microgrids for sustainable power afford localized energy independence, unlike electrification from centralized grids, which can be disrupted by incidents like natural catastrophes, cyberattacks, equipment malfunctions, etc. These systems secure energy for buildings and small communities, operating in an off-grid mode. Furthermore, they provide a reliable backup power source in the event of an emergency, ensuring that critical infrastructure remains operational.
- Flexibility and Scalability
Hydrogen microgrids for sustainable power are very versatile, capable of meeting a wide range of energy needs at varying scales. Normally, these systems are paired with renewable energy systems such as solar or wind to generate hydrogen via electrolysis.
This hydrogen is then stored in tanks and can be used during an outage or periods of electricity shortage from renewables to supply power to fuel cells.
- Long-Duration Energy Storage
However, the real attraction of a hydrogen microgrid rests in their ability to keep energy stored for long periods of time. Hydrogen, unlike batteries, can be stored for an indefinite period without any diminution in energy. So, hydrogen microgrids are an excellent solution to reconcile fluctuating demand with intermittent renewable energy supplies.
Applications of Hydrogen Microgrids
The versatility of hydrogen microgrids makes them suitable for a variety of applications, addressing energy challenges across sectors and geographies.
- Remote and Off-Grid Communities
In remote places where expanding the main grid is not economically possible, hydrogen microgrids provide a dependable and sustainable source of electricity. Their modular architecture also makes it easy for them to expand, allowing them to meet increasing energy demands.
- Critical Infrastructure
Government buildings, data centers, and hospitals require continual power to function properly. In the case of an emergency or a grid outage, hydrogen microgrids provide a dependable backup power source, ensuring company continuity. Their long-term storage capacity makes them ideal for critical applications.
- Industrial and Commercial Facilities
Hydrogen microgrids can increase energy dependability and reduce carbon emissions in commercial and industrial buildings. These microgrids contribute to business sustainability goals by permitting seamless transitions to sustainable energy sources via interaction with existing energy systems.
- Disaster Recovery
Hydrogen microgrids can provide emergency power to affected populations after natural disasters. They are highly beneficial for disaster response and recovery operations because of their rapid deployment and independence from centralised infrastructure.
Technological Innovations Driving Hydrogen Microgrids
The development of hydrogen microgrids is based on a variety of technological advancements that improve their efficiency, dependability, and economic feasibility.
- Advanced electrolysis systems
Electrolysis just got more costly-and efficient. Modern electrolyzers are, in fact a critical element to the success of hydrogen microgrids, designed to mainly convert renewable electricity to hydrogen with minimal energy losses. They ensure that hydrogen production is sustainable and economical.
Improvements in material science and engineering have led to enhanced fuel cell performance. Hydrogen microgrids can provide continuous electricity for long periods of time since their high-efficiency fuel cells are more durable and cost-effective. Solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) are an important advancement in stationary applications.
- Digital Integration
Hydrogen microgrid operations are changing due to the usage of digital technology such as IoT sensors and improved monitoring tools. Real-time data analytics allows for predictive maintenance, energy production optimization, and improved system reliability. Microgrid performance is also being simulated and optimised using digital twin technology, which generates virtual representations of real-world systems.
Sustainability and Long-Term Vision
More than just a technological innovation, hydrogen microgrids offer a path to a robust and resilient energy future.
Hydrogen microgrids will gain prominence as technology, law, and collaboration advance. The construction of hydrogen hubs in locations with concentrated production, storage, and consumption will speed up adoption and result in integrated ecosystems that boost the fuel’s value.
Conclusion
Hydrogen microgrids are an innovative way to address the world’s energy needs. These systems, which incorporate sustainability, adaptability, and resilience, offer an alternative to traditional energy sources. Hydrogen microgrids for sustainable power can help to battle climate change while providing electricity to communities, industry, and critical infrastructure.
As the world moves toward clean energy, hydrogen microgrids will be crucial to supplying a strong, decentralized, and sustainable electricity infrastructure. By investing in this revolutionary technology, we can create a future where everyone has access to reliable, clean energy.